
Veterinary-grade artificial insemination equipment includes advanced tools and technologies designed for precise reproductive procedures in animals. These systems play a vital role in both farms and clinics by improving productivity, animal welfare, and sustainability. Artificial insemination technology offers immediate benefits:
- AI approaches in pig farming increase operational efficiency and reproductive outcomes.
- Wearable and implantable sensors enable early disease detection and continuous welfare monitoring, supporting better farm management.
Practitioners and producers see measurable gains in both animal health and day-to-day operations.
Key Takeaways
- Veterinary AI equipment improves animal reproduction by enhancing genetics, reducing disease risks, and increasing farm productivity.
- Choosing the right AI tools depends on animal species, farm size, and technical needs to ensure effective and efficient use.
- Proper handling, thawing, and insemination techniques are vital for maximizing pregnancy success and maintaining semen quality.
- Advanced technologies like AI imaging, automated monitoring, and robotic tools support precise procedures and better animal welfare.
- Reliable suppliers, good warranty coverage, and ongoing training help maintain equipment performance and ensure long-term success.
Artificial Insemination in Veterinary Practice
Key Benefits of AI Technology
Artificial insemination technology delivers significant advantages in veterinary medicine. This approach allows veterinarians and producers to access superior genetics, which accelerates genetic improvement in herds. By using semen from high-quality males, farms can enhance traits such as milk production, calving ease, and disease resistance. The technology also reduces the need for maintaining large numbers of breeding males, which lowers operational costs and simplifies herd management.
Artificial insemination helps control the spread of infectious diseases by minimizing animal transport and direct contact. Semen extenders with antibiotics further reduce the risk of bacterial transmission. Frozen semen technology enables long-distance transport and the use of valuable genetics even after the donor animal’s lifetime.
Scientific studies show that proper semen handling, technician training, and the use of advanced protocols improve pregnancy rates and overall reproductive success. Economic benefits include higher calf values, more uniform groups for marketing, and reduced losses from failed conceptions. Farms that synchronize estrous cycles and use artificial insemination often see more efficient calving seasons and increased revenue.
Common Applications in Farm and Clinic Settings
Artificial insemination finds its primary application in dairy farm settings. Here, trained veterinarians or AI technicians use specialized equipment to deposit semen into female animals as part of herd reproductive management. The dairy industry benefits most from this technology due to the ability to freeze and transport bovine semen, which supports genetic improvement and better record keeping.
- Dairy farms: Over 60% of U.S. dairy cows are bred using artificial insemination, leading to improved milk production and herd quality.
- Clinical settings: Veterinarians use artificial insemination for reproductive management, genetic selection, and training purposes. Models and simulators help students and practitioners develop critical skills while reducing animal stress.
- Swine and equine breeding: The technology is also common in pig and horse breeding, especially for high-value animals like racehorses.
- Sheep and poultry: Use is less frequent due to anatomical and economic factors, but advances in laparoscopic techniques have improved outcomes in sheep.
Recent trends show increased adoption of timed artificial insemination protocols, especially in large-scale dairy operations, which further boosts reproductive efficiency and herd fertility.
Essential Equipment Checklist
Insemination Guns and Applicators
Insemination guns and applicators serve as the cornerstone of any veterinary-grade artificial insemination setup. These devices deliver semen directly into the reproductive tract with precision and consistency. Modern insemination guns feature advanced materials such as stainless steel, plastic, or hybrid combinations. Stainless steel options offer durability and compatibility with high-pressure steam sterilization, ensuring both hygiene and longevity. Plastic components provide lightweight handling but require chemical sterilization due to heat sensitivity. Hybrid designs combine the best of both worlds, optimizing user comfort and durability.
Recent advancements include ergonomic improvements like finger supports and quick-lock mechanisms. These features enhance efficiency and reduce user fatigue during repetitive procedures. Many insemination guns now support a range of semen straw types, including French Mini and Medium straws, as well as split or non-split sheaths. Adjustable settings for insemination depth, volume, and pressure allow veterinarians to tailor procedures for different animal species. Integrated sensors monitor pressure and temperature, while data logging capabilities record insemination parameters for quality control. Wireless connectivity enables seamless data transfer to practice management systems.
Tip: Always select an insemination gun that matches the specific needs of your practice or farm. Consider compatibility with various catheters and accessories, as well as ease of sterilization and ergonomic design.
A complete insemination kit should also include sheaths to cover the gun, gloves for hygiene, and training resources to ensure proper technique.
Semen Straws and Storage Containers
Semen straws play a critical role in preserving and delivering genetic material during artificial insemination. These straws, typically made from biocompatible plastics, store semen in precise volumes and protect it from contamination. Before use, technicians thaw frozen semen straws to prepare them for deposition.
Proper storage is essential to maintain semen viability. Storage containers, often called canisters, feature cylindrical designs with handles for easy manipulation inside Dewar flasks. The base of each canister includes holes or grates to allow liquid nitrogen flow, ensuring consistent cooling. Insulation materials such as Cryogel® help maintain thermal stability and protect semen from temperature fluctuations.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Holes/grates at base | Consistent liquid nitrogen flow |
| Insulation materials | Maintains thermal stability |
| Handles | Easy manipulation and secure placement |
| Secure hooks | Prevents accidental spills |
Minimizing exposure time to ambient temperature is crucial. Technicians should remove semen straws from storage for only a few seconds to prevent thermal damage. Proper handling protocols and equipment designed to maintain the cold chain help preserve semen viability, especially for sensitive structures like the acrosome.
Thawing Devices and Temperature Control
Thawing devices ensure that semen reaches the optimal temperature for successful artificial insemination. Electric thaw baths remain the preferred choice for consistent temperature control. These devices maintain water temperatures between 94°F and 98°F, and require regular calibration to ensure accuracy. Proper thawing prevents thermal shock and preserves sperm viability.
Best practices for thawing include:
- Maintain thaw water temperature between 90°F and 95°F for at least 40 seconds.
- Avoid thawing semen straws in pockets or inside the animal, as this leads to slow thaw rates and reduced sperm viability.
- Dry semen straws thoroughly after thawing to prevent water-induced sperm damage.
- Minimize the time semen spends out of liquid nitrogen; use tweezers and keep removal time under 10 seconds.
- When thawing multiple straws, use more than 1 quart of water and agitate to prevent freezing together.
- Warm the insemination gun before loading semen to avoid cold shock.
- Regularly calibrate thermometers to ensure accurate temperature monitoring.
Some clinics use rapid thawing at higher temperatures for improved sperm viability, but this method requires precise timing to avoid overheating. Dry thawing devices offer portability and reduce contamination risk, though they may involve higher initial costs.
Note: Reviewing semen handling procedures before each breeding season helps prevent errors and maximizes reproductive success.
Diagnostic Imaging Systems
Diagnostic imaging systems have become essential in modern veterinary reproductive management. These systems help veterinarians visualize reproductive organs, assess animal health, and improve the success rate of procedures. In the context of artificial insemination, imaging tools provide real-time feedback and support accurate decision-making.
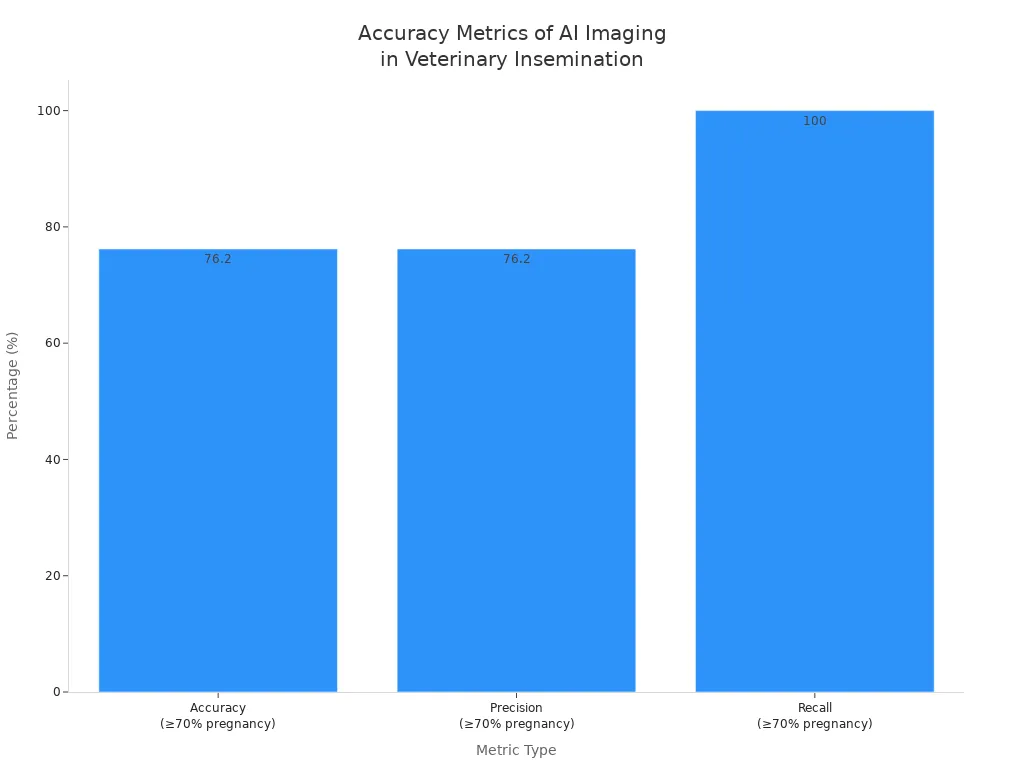
Recent advancements focus on AI-assisted imaging. One leading method uses a dedicated camera to capture images of the external uterine opening during insemination. The system then analyzes these images with a convolutional neural network, such as EfficientNetB1, to predict pregnancy probability. This approach offers high accuracy and supports veterinarians in optimizing insemination timing.
| Diagnostic Imaging System Type | Description | Accuracy Metrics (at ≥70% pregnancy probability) | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-assisted external uterine opening imaging | Uses images of the external uterine opening captured by a dedicated camera during insemination. | Accuracy: 76.2% | Portable, smartphone app-based, requires minimal technical skill, real-time use. |
| (Convolutional Neural Network – EfficientNet) | Employs EfficientNetB1 CNN model for pregnancy probability prediction to optimize insemination. | Precision: 76.2% | Accuracy varies by breed: 61.5% for Holstein, 100% for Japanese Black cows (data not shown). |
| Recall: 100% | Image quality critical; out-of-focus images reduce accuracy. Future improvements include auto-capture. |
Traditional imaging methods, such as ultrasound and radiography, remain reliable for reproductive assessment. However, these methods often require more technical skill and are less practical for large-scale or field use. AI-based imaging systems offer portability, real-time analysis, and user-friendly interfaces, making them suitable for both clinics and farms.
Note: Image quality plays a critical role in diagnostic accuracy. Veterinarians should ensure proper camera focus and lighting during procedures.
Automated Monitoring Devices
Automated monitoring devices have transformed reproductive management by providing continuous, real-time data on animal health and reproductive cycles. These devices use advanced sensors and wireless communication to track physiological and behavioral changes, supporting timely interventions and reducing manual labor.
- The e-Synch system stands out as a leading solution for cattle reproductive management. This device integrates intravaginal hormone delivery with sensors that monitor temperature and activity. It communicates remotely through an IoT platform, allowing veterinarians to program and monitor the device from a distance.
- The e-Synch system automates hormone delivery, reducing the need for manual injections and minimizing animal discomfort. It collects sensor data and transmits it to a controlling app, streamlining the synchronization of reproductive cycles.
- Earlier devices, such as the drug release and monitoring unit (DMU), offered basic sensing and wireless control. However, they lacked the comprehensive integration and remote capabilities found in the e-Synch system.
- In vivo studies confirm the e-Synch device’s ability to dispense hormones automatically and collect accurate sensor data. The system addresses challenges such as labor-intensive protocols and synchronization complexity by automating key steps.
Veterinarians and producers benefit from these devices by improving reproductive efficiency, reducing errors, and enhancing animal welfare. Automated monitoring devices represent a significant advancement in the field, especially for large herds and intensive operations.
AI-Powered Analysis Software
AI-powered analysis software has revolutionized the evaluation of reproductive health and semen quality in veterinary practice. These tools use advanced algorithms to automate image analysis, deliver precise measurements, and accelerate workflows.
One example, BovIntel, automatically detects and labels reproductive structures such as ovaries, follicles, and corpus luteum during ultrasound scans. The software provides measurements accurate to the nearest millimeter and enables scanning up to three times faster than traditional methods. Users of all experience levels can benefit from its intuitive interface, and the software integrates seamlessly with existing ultrasound devices.
AI-powered analysis software offers several advantages over traditional methods:
| Feature/Aspect | Traditional Methods (Microscopy, CASA) | AI-Powered Analysis Software |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High; expensive equipment and skilled operators needed | Low-cost solutions (e.g., $476 system) |
| Portability | Limited; bulky and lab-bound | Portable; uses Raspberry Pi and microfluidic chips |
| Automation | Manual or semi-automated requiring expert input | Fully automated with AI models (CNN, EfficientDet-Lite) |
| Accuracy | Gold standard; objective and precise | Comparable accuracy to CASA; validated statistically |
| Speed | Time-consuming; requires lab processing | Rapid analysis (e.g., 1 minute per 30 frames at 30 fps) |
| Accessibility | Limited to labs and skilled personnel | Accessible for on-site use, suitable for smallholder farmers |
| Sample Handling | Manual sample prep | Integrated microfluidic chips for precise handling |
| Hardware Requirements | Expensive microscopes and PCs | Low-cost hardware platforms like Raspberry Pi |
AI-powered software improves early detection of fertility issues, enabling interventions up to 35 days earlier than conventional pregnancy scans. This technology enhances decision-making and reproductive efficiency, potentially increasing profitability for farmers. The combination of laboratory-grade accuracy, portability, and affordability makes AI-powered analysis software a valuable asset for both clinics and farms engaged in artificial insemination.
Tip: Integrating AI-powered analysis software into daily practice can streamline workflows and support better reproductive outcomes.
Robotic Surgical Tools
Robotic surgical tools have transformed veterinary reproductive procedures. These advanced instruments deliver precision, control, and consistency that surpass traditional manual techniques. Veterinarians rely on robotic systems to perform delicate tasks such as embryo transfer, laparoscopic insemination, and minimally invasive surgery.
Modern robotic platforms feature articulated arms, high-definition cameras, and intuitive control interfaces. Surgeons manipulate instruments with enhanced dexterity, reducing tissue trauma and improving recovery times. The technology supports complex maneuvers in confined anatomical spaces, which proves essential for species with challenging reproductive anatomy.
Key Advantages of Robotic Surgical Tools:
- Enhanced Precision: Robotic arms execute micro-movements with accuracy, minimizing human error.
- Reduced Fatigue: Automated systems handle repetitive tasks, allowing veterinarians to focus on decision-making.
- Improved Visualization: Integrated imaging provides real-time feedback, supporting optimal placement of semen or embryos.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Smaller incisions lead to faster healing and lower infection risk.
Veterinary clinics and research facilities use robotic tools for laparoscopic insemination in sheep and goats, where manual access is limited. Swine breeding programs benefit from robotic assistance during embryo transfer, increasing success rates and reducing stress for animals.
Tip: Clinics should evaluate the compatibility of robotic systems with existing imaging and monitoring devices. Training staff on robotic platforms ensures safe and effective operation.
| Feature | Benefit | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Articulated arms | Greater dexterity | Laparoscopic insemination |
| HD cameras | Clear visualization | Embryo transfer procedures |
| Automated controls | Consistent technique | Minimally invasive surgery |
| Sterilizable surfaces | Infection prevention | All reproductive procedures |
Veterinarians who adopt robotic surgical tools report higher procedural success and improved patient outcomes. The investment in robotics reflects a commitment to excellence and innovation in animal care.
Practice Management Software
Practice management software streamlines operations in veterinary clinics and farm settings. These digital platforms organize patient records, schedule appointments, and track inventory. Efficient management systems support reproductive programs by integrating data from AI equipment, diagnostic imaging, and monitoring devices.
Veterinarians use practice management software to record insemination dates, monitor pregnancy outcomes, and analyze herd performance. The software generates reports that guide breeding decisions and resource allocation. Automated reminders help staff maintain timely follow-ups and routine health checks.
Core Features of Practice Management Software:
- Patient Database: Stores medical histories, reproductive cycles, and treatment plans.
- Scheduling Tools: Coordinates appointments, procedures, and technician assignments.
- Inventory Management: Tracks supplies such as semen straws, hormones, and surgical instruments.
- Integration Capabilities: Connects with AI-powered analysis software and automated monitoring devices.
Note: Selecting software with cloud-based access allows veterinarians to update records from any location. Data security features protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with veterinary regulations.
Veterinary teams benefit from centralized data management. The software reduces paperwork, minimizes errors, and improves communication among staff. Farms with large herds use management platforms to synchronize breeding schedules and optimize reproductive efficiency.
| Function | Benefit | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Patient tracking | Accurate health records | Monitoring estrous cycles |
| Automated reminders | Timely interventions | Scheduling inseminations |
| Data analytics | Informed decision-making | Evaluating pregnancy rates |
| Inventory alerts | Prevents shortages | Ordering semen straws |
Practice management software supports the integration of advanced AI equipment into daily workflows. Veterinary professionals who leverage these tools achieve higher productivity and deliver superior care to their patients.
How to Choose the Right Equipment
Assessing Species and Patient Needs
Veterinary professionals must evaluate the anatomical and physiological differences among animal species before selecting artificial insemination equipment. Sheep, for example, have a tortuous cervix that often requires laparoscopic insemination or specialized catheters. Cattle typically use frozen semen, while small ruminants may need fresh or chilled semen due to lower tolerance for freezing. Sperm processing protocols also vary, so equipment must match the species’ requirements for semen handling and deposition.
- Anatomical challenges, such as the sheep cervix, drive innovation in catheter design.
- Semen storage methods differ, influencing the choice of storage containers and thawing devices.
- Sire fertility and semen quality affect compatibility with handling protocols.
- Skilled personnel and suitable facilities, including handling chutes and refrigeration, support successful AI procedures.
- Management practices, such as herd health and nutrition, maximize reproductive outcomes.
Veterinarians should tailor equipment choices to the species and patient needs to ensure optimal results.
Matching Equipment to Scale and Setting
The scale of a farm or clinic influences the complexity and type of AI equipment required. Large commercial operations benefit from advanced systems that support high-throughput insemination and data management. Smaller farms may prioritize cost-effective solutions and ease of use.
| Factor | Description & Impact |
|---|---|
| Financial Cost | AI procedures range from $25 to $100 per cow; equipment and training add to upfront costs. |
| Technical Expertise | Skilled operators are essential, especially for advanced techniques like laparoscopic AI. |
| Herd Size & Breeding Scale | Larger herds justify investment in automated and high-capacity equipment. |
| Timing & Synchronization | Efficient estrus synchronization improves AI success, especially in large-scale settings. |
| Genetic Improvement Goals | Operations focused on genetic gains may require specialized equipment for precise semen delivery. |
Innovations in catheter design and hormone delivery systems help overcome anatomical and management challenges. Matching equipment to the operation’s scale ensures efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Evaluating Features and Specifications
Selecting veterinary-grade AI equipment involves careful consideration of technical features and specifications. Modern insemination guns offer digital interfaces for real-time monitoring and control. Adjustable settings for depth, volume, and pressure accommodate different breeds and conditions. Integrated sensors track pressure and temperature, ensuring optimal insemination environments.
- Data logging capabilities support breeding management and traceability.
- Wireless connectivity enables remote access and analysis.
- Ergonomic, lightweight designs reduce operator fatigue.
- Battery-powered operation allows use in remote locations.
- Durable construction with medical-grade materials ensures longevity.
- Hygienic, detachable components simplify cleaning and sterilization.
- Compatibility with various catheters and accessories increases versatility.
Key specifications, such as probe rod length (350mm), diameter (22mm), and working channel size (11mm), contribute to precision and comfort. Features like a 3.5-inch screen and high-resolution camera enhance visualization during procedures. Veterinary professionals should prioritize equipment that supports accuracy, efficiency, and animal welfare.
Best Practices for Use and Maintenance
Proper Installation and Setup
Veterinary professionals achieve optimal results by following precise installation and setup procedures for artificial insemination equipment. They begin by thoroughly cleaning and sanitizing all tools before use. Warming and handling AI catheters with care prevents contamination and ensures comfort for the animal. Practitioners use protective sleeves and gloves to maintain hygiene throughout the process. During insemination, the catheter should be inserted gently through the cervix, stopping when about half an inch to an inch of the catheter is inside the uterine body. This careful placement avoids irritation and reduces the risk of injury. Depositing semen slowly over three to five seconds, without moving the catheter, helps maximize conception rates. Training and hands-on practice, such as attending AI courses or working alongside experienced professionals, build the necessary skill for consistent success.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Routine maintenance extends the lifespan of AI equipment and preserves semen viability. Professionals store semen tanks in secure, dry locations, away from corrosive chemicals, and monitor liquid nitrogen levels regularly, ensuring at least three inches remain at all times. They check for frost buildup, which can signal seal failure. Before insemination, they thaw semen straws in water at 90–95°F for about 40 seconds, using a thermometer and timer for accuracy. Only one straw is thawed at a time unless multiple inseminations occur within 15 minutes. After thawing, straws are dried and used promptly. Practitioners sanitize the vulva area, use sterile sheaths on insemination guns, and store equipment in closed containers. Accurate inventory records and regular cleaning routines help maintain sterility and efficiency.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Safety and compliance remain central to veterinary artificial insemination. Facilities must provide clean, ventilated environments for animals, with proper nutrition and health monitoring. Personnel wear protective clothing and footwear to minimize pathogen transmission. Disease surveillance protocols require isolation and regular testing of breeding animals. All AI equipment, including artificial vaginas and collection areas, undergoes thorough cleaning and disinfection before and after use. Facilities feature guard rails and safe footing to protect both animals and handlers. Only trained professionals perform specialized procedures, ensuring adherence to animal welfare laws, biosecurity standards, and occupational safety regulations.
Consistent attention to installation, maintenance, and safety protocols supports successful outcomes and upholds the highest standards in veterinary practice.
Sourcing and Purchasing Tips
Identifying Reputable Suppliers
Veterinary professionals should prioritize reputable suppliers when sourcing artificial insemination equipment. Reliable suppliers demonstrate a commitment to quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. Key criteria include:
- Ergonomic and user-friendly designs that reduce technician fatigue and improve operational efficiency.
- Customization options for materials, such as medical-grade stainless steel or plastics, to meet hygiene and durability needs.
- Consideration of animal breed and size to ensure appropriate design and minimize injury risk.
- Compliance with international veterinary standards, including ISO 13485 certification and veterinary-specific regulations like FDA-CVM clearance or EMA standards.
- Validated sterilization protocols and performance benchmarks, such as conception rates and contamination prevention.
- Warranty terms and clear documentation that meet regulatory requirements.
- Availability of spare parts and technical support, including 24-hour veterinary consultation hotlines.
- Verified supplier experience and high ratings from previous buyers.
Suppliers who offer transparent quality control, rigorous testing, and comprehensive after-sales support stand out in the market.
Comparing Product Quality and Service
Comparing equipment providers involves evaluating both product quality and after-sales service. The following table summarizes essential benchmarks:
| Benchmark Category | Key Metrics / Indicators |
|---|---|
| Product Quality | Durability, reliability, conception success rates, precise engineering, contamination prevention features |
| Performance Metrics | Conception rate (>28%), insertion depth accuracy (±2mm), contamination prevention (disposable sheaths) |
| Cost Efficiency | Durability (5+ years), sterilization costs, consumable expenses, bulk pricing discounts |
| Quality Assurance | Third-party validation, ISO certifications, IP67 waterproofing, warranty (≥2 years) |
| Integration Capabilities | Compatibility with farm management software via Bluetooth/API |
| After-Sales Service | Service network coverage, spare parts availability (within 72 hours), technician training, manuals, videos |
| After-Sales KPIs | Complaint resolution time, customer satisfaction, warranty cost as % of revenue |
| Logistics & Reach | Shipping speed, product availability, global distribution network |
| Supplier Comparison | Production capacity, risk factors, environmental impact, buyer experience |
Providers who meet these benchmarks deliver consistent performance and long-term value.
Understanding Warranty and Support
Warranty terms and support services protect buyers and ensure reliable operation. The table below outlines typical offerings:
| Equipment Type | Warranty/Return Terms | Support Services Provided | Buyer Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reproduction Units/Bundles for Veterinarians | 12 months manufacturer warranty; repair or replacement | Manufacturer technical department support | Buyer pays shipping for defective parts |
| Visual Insemination Guns | Replacement if defective within 15 business days | Replacement based on manufacturer decision | Buyer pays shipping for defective items return |
| Immunoassay Systems | 14-day return guarantee with technician cooperation | Email, social media support, training videos | Customer pays return shipping, keep packaging |
| Electrical/Bodily Fluid Devices | Replacement only if defective within warranty period | Replacement only | Buyer pays shipping for defective items return |
Buyers should review warranty periods, return policies, and support channels before making a purchase. Responsive support and clear warranty coverage contribute to a positive ownership experience.
Troubleshooting and Compliance
Common Issues and Solutions
Veterinary professionals often encounter several challenges when using artificial insemination equipment. One technical issue involves lower success rates with frozen semen. Transcervical insemination techniques, which visually guide the catheter through the cervix, have improved success rates up to 80%. This approach offers a less invasive alternative to surgical insemination, especially in canine reproduction.
Other frequently reported issues include the high cost of advanced AI technologies and equipment. This barrier can limit adoption, particularly for small-scale farms or operations in developing regions. Lack of expertise and training among veterinary staff also impacts the effectiveness of artificial insemination procedures.
To address these challenges, many organizations invest in comprehensive training and education programs. These initiatives help close knowledge gaps and ensure proper use of equipment. Companies continue to develop improved products and provide robust customer support, including hands-on training and technical assistance. Integrating advanced genetic and precision breeding technologies further enhances efficiency and success rates. Emphasizing best practices—such as proper insemination techniques, synchronization protocols, and optimal animal nutrition—also contributes to better outcomes.
Tip: Regularly scheduled training sessions and refresher courses help maintain high standards and reduce procedural errors.
Meeting Veterinary Standards and Regulations
Compliance with veterinary standards and regulations ensures the safety and effectiveness of artificial insemination procedures. Facilities must provide designated areas for holding donor animals, embryo collection, processing, storage, and cleaning or sterilization of equipment. Construction materials in these areas should resist moisture and withstand repeated cleaning.
All procedures, including artificial insemination, require supervision by a qualified veterinarian. Personnel must wear clean garments, disinfected boots, and scrub hands thoroughly before entering workspaces. Donor animals must reside in approved facilities and undergo testing to confirm freedom from communicable diseases. Additional certifications may apply based on disease prevalence, breeding methods, or semen source.
Equipment used for artificial insemination must be cleaned, disinfected, or sterilized in designated areas that meet strict hygiene standards. Regulatory officials, such as those from the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, have access to all relevant areas for oversight. Technicians performing artificial insemination must hold appropriate permits and qualifications, ensuring professional standards and animal welfare.
Note: Adhering to these regulations not only protects animal health but also upholds the reputation and credibility of veterinary practices.
Veterinary professionals and producers should prioritize equipment that meets species-specific needs, operational scale, and technical requirements. High-quality AI tools deliver lasting benefits, including improved genetics, enhanced reproductive efficiency, and reduced disease risks. Reliable service and ongoing support ensure consistent performance and long-term value.
Next steps for successful implementation:
- Attend hands-on AI training programs with live animal practice.
- Master semen handling and thawing techniques.
- Focus on accurate heat detection and insemination timing.
- Maintain robust herd health and nutrition programs.
- Invest in continuous skill development for technicians.
Commitment to excellence in equipment selection and management drives sustainable success in veterinary reproduction.
FAQ
What factors should buyers consider before purchasing veterinary AI equipment?
Buyers should evaluate species compatibility, equipment durability, supplier reputation, and after-sales support. They should also check for compliance with veterinary standards and ensure the equipment matches their operational scale.
How often should veterinary AI equipment undergo maintenance?
Routine maintenance should occur after every use. Technicians must clean, disinfect, and inspect all components. Regular checks help prevent malfunctions and extend equipment lifespan.
Can AI equipment integrate with existing farm management software?
Most modern AI equipment supports integration with farm management platforms. Buyers should confirm compatibility with their current systems before purchase to ensure seamless data transfer and workflow efficiency.
What training is required to operate veterinary-grade AI equipment?
Operators need hands-on training, often provided by suppliers or through certified courses. Proper training ensures safe use, accurate procedures, and optimal animal welfare.
How does warranty coverage typically work for AI equipment?
Warranty terms vary by supplier. Most offer a 12-month manufacturer warranty covering repairs or replacements. Buyers should review warranty details and understand their responsibilities regarding shipping and maintenance.
Post time: Aug-13-2025
